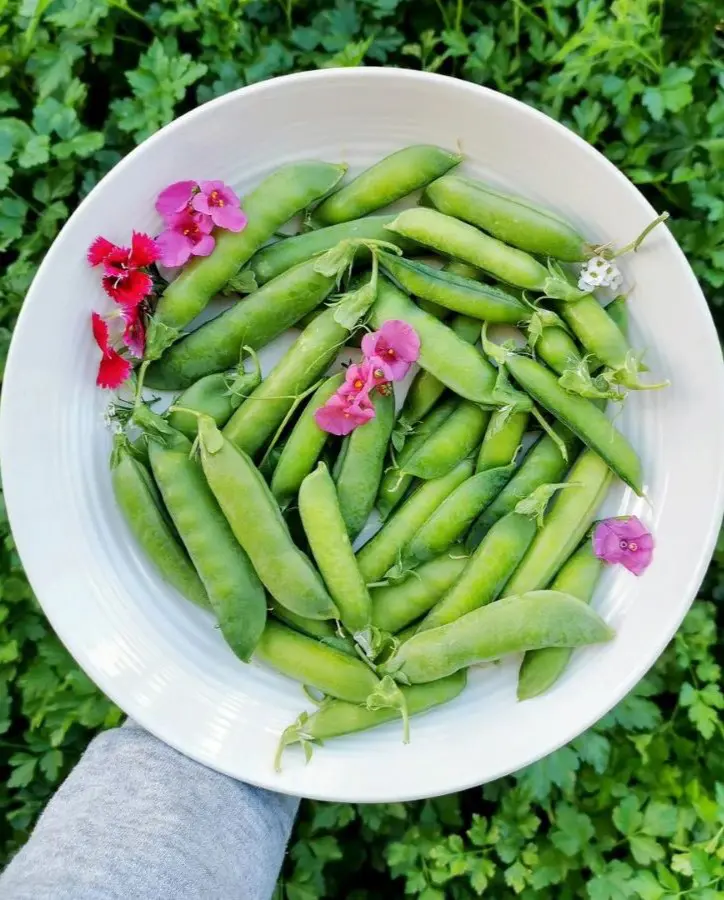
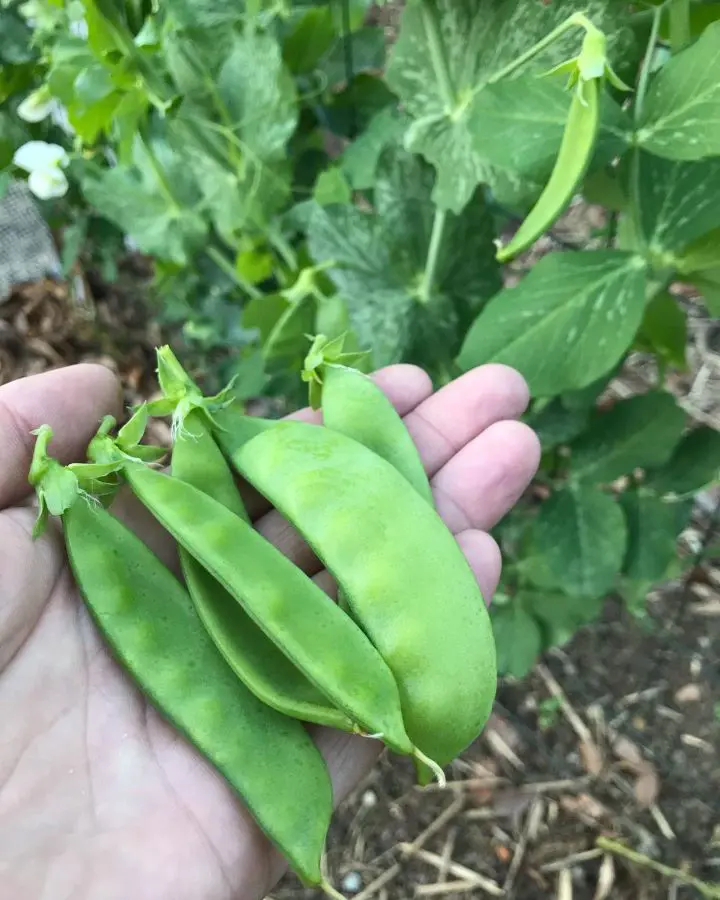
How To Store Peas After Picking
Peas, like any other produce, should ideally be consumed right after harvesting. This is because the sugar in peas turns into starch, which browns them as they start perishing.
If you cannot finish them, you should store them properly. Proper storage is essential in preserving the freshness and flavor of your peas.
Storing Unshelled Peas
Gently pull off the tips of the beans to remove the tough strings that are inedible. Store fresh ones in a breathable container or perforated plastic bag. These plastic bags have tiny holes evenly distributed across the bag.
The holes prevent moisture buildup. Excess moisture can lead to mold and bacteria. Store them in the crisper drawer of your refrigerator. This compartment allows you to regulate the moisture content around the peas and prevent them from drying out or becoming overly moist.
- It also helps prevent external odors and contaminants from affecting the peas.
- Unshelled peas should be consumed within a few days for optimal flavor
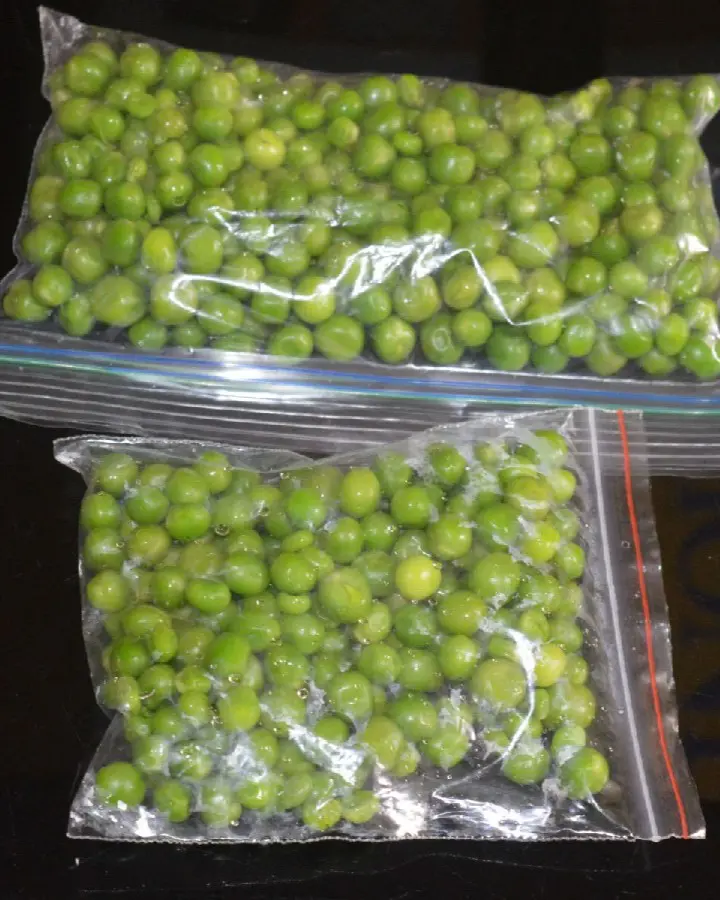

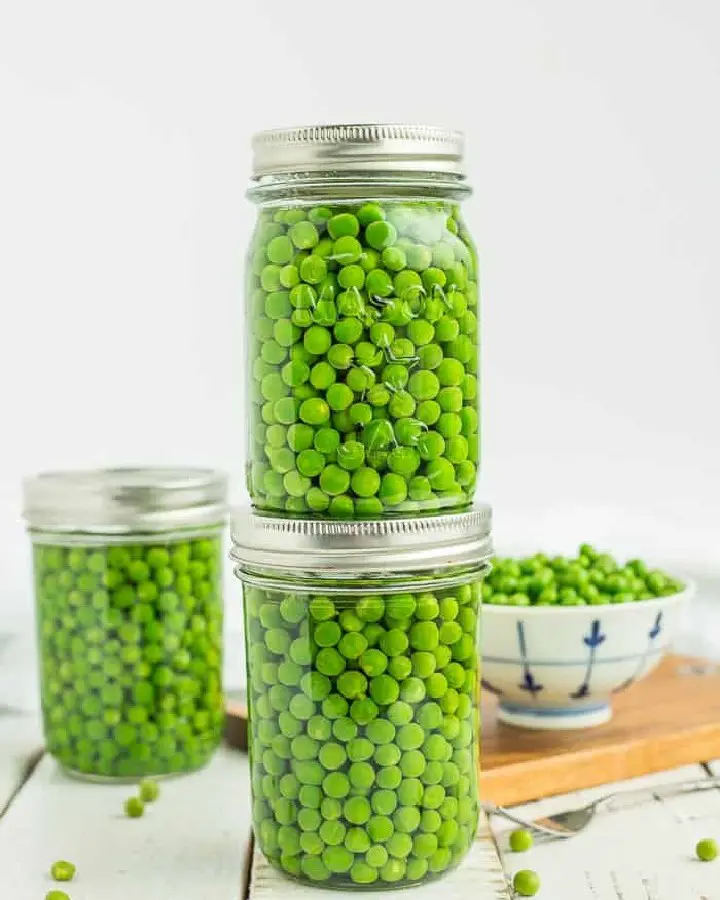
Storing Shelled Peas
- Remove peas from their skin.
- Heat water in a pan and let it boil. Put peas in water for 2 minutes.
- Separate the peas from the water with a colander.
- Prepare ice-cold water by mixing ice and water in a bowl.
- Toss boiled peas in ice water and keep them in the bowl until the peas have cooled down.
- Strain the peas, place them in a perforated plastic bag or container, and refrigerate.
- Shelled peas will stay fresh for about a week in the refrigerator.
Maintaining the freshness of peas requires careful temperature control. In the refrigerator, they should be stored between 32°F (0°C) and 40°F (4.4°C).